比赛链接
Dashboard - Educational Codeforces Round 151 (Rated for Div. 2) - Codeforces
A-Forbidden Integer
题意:给定一个数字n,要求能否从1到k中任意选择数(不能选择1到k的一个数x,每个数可以选择0到无穷次)的和等于n(1<=x<=k<=n)
思路:任何正整数都是1的倍数,所以当x!=1时,只需选择n个1即可。
当x等于1时,若k也等于1,此时无可供选择的数,无法组成。又知道,任意大于1的数都可以通过2,3两个数得到(奇偶性,非奇即偶)。所以只需讨论k=2和k>=3两种情况。k=2时,只能组成偶数,k=3时,组成任何大于等于2的数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve(int n,int k,int x)
{
int count=0;
if(x!=1)
{
printf("YES\n");
count=n;
printf("%d\n",count);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("1 ");
}
printf("\n");
}
else
{
if(k==1)
{
printf("NO\n");
}
else if(k>=3&&n%2==1)
{
printf("YES\n");
int x=n/2;
count=x;
printf("%d\n",count);
for(int i=1;i<=count-1;i++)
{
printf("2 ");
}
printf("3\n");
}
else if(k>=3&&n%2==0)
{
printf("YES\n");
int x=n/2;
count=x;
printf("%d\n",count);
for(int i=1;i<=count;i++)
{
printf("2 ");
}
printf("\n");
}
else
{
if(n%2==1)
{
printf("NO\n");
}
else
{
printf("YES\n");
count=n/2;
printf("%d\n",count);
for(int i=1;i<=count;i++)
{
printf("2 ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
int n,k,x;
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&x);
solve(n,k,x);
}
return 0;
}
|
B-Come Together
简单题 略
C-Strong Password
题意:给出两个长度为m的字符串a,b(都为数字),要求密码对应位的数字介于 ai,bi 之间,且密码不能是字符串base的子序列。求问能否找到这样一串的密码。
思路:这道题一开始我思路就跑偏了,用的DFS做。但题目只需要求找到一串,所以不用判断所有的字符串是否满足。那么我们只需分析最有可能是密码的特征是什么,针对这一串密码检验就好。将密码的m位依次来看,第i位密码在base中出现的位置一定在 i−1位置之后,我们要越可能得到密码,那么我们就需要当前第i位数字在base中的位置越往后越好,这样密码才不容易是base的子序列。
贪心
- 对于第i位,遍历密码可能的每个数字,判断该数字在base中出现的位置
- 取在base最靠后的位置作为第i+1位的接着判断的base开始位
- 如果i<m时,已经超过了base的长度那么这串密码不是base的子序列
时间复杂度:O(nmD)D=l−r
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int tag=0;
int ans[11];
int ne[10];
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
tag=0;
string base;
cin>>base;
int m;
cin>>m;
string a;
string b;
cin>>a>>b;
int k=0;
int n=base.size();
ne[0]=-1;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int l=a[i-1]-'0';
int r=b[i-1]-'0';
int k_r=ne[i-1]+1;
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++)
{
int k=ne[i-1]+1;
while(k<n&&(base[k]-'0')!=j) k++;
k_r=max(k,k_r);
}
ne[i]=k_r;
if(k_r>=n)
{
tag=1;
break;
}
else if(k_r==n-1&&i<=m-1)
{
tag=1;
break;
}
}
if(tag==0)
{
printf("NO\n");
}
else
{
printf("YES\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
|
进一步思考,while循环内的查找能否在O(1)的时间复杂度做到呢?对于从某个位置开始往后查找特定的数字,我们可以预处理一个数组 next[i][j] 表示从第i位开始的下一个数字j的位置,该步时间复杂为O(nD)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| for(int j=0;j<10;j++)
{
if(j!=s[n-1]-'0')
ne[n-1][j]=n;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ne[i][s[i]-'0']=i;
}
for(int i=n-1;i>=1;i--)
{
for(int j=0;j<10;j++)
{
if(j!=s[i-1]-'0')
ne[i-1][j]=ne[i][j];
}
}
|
D-Rating System
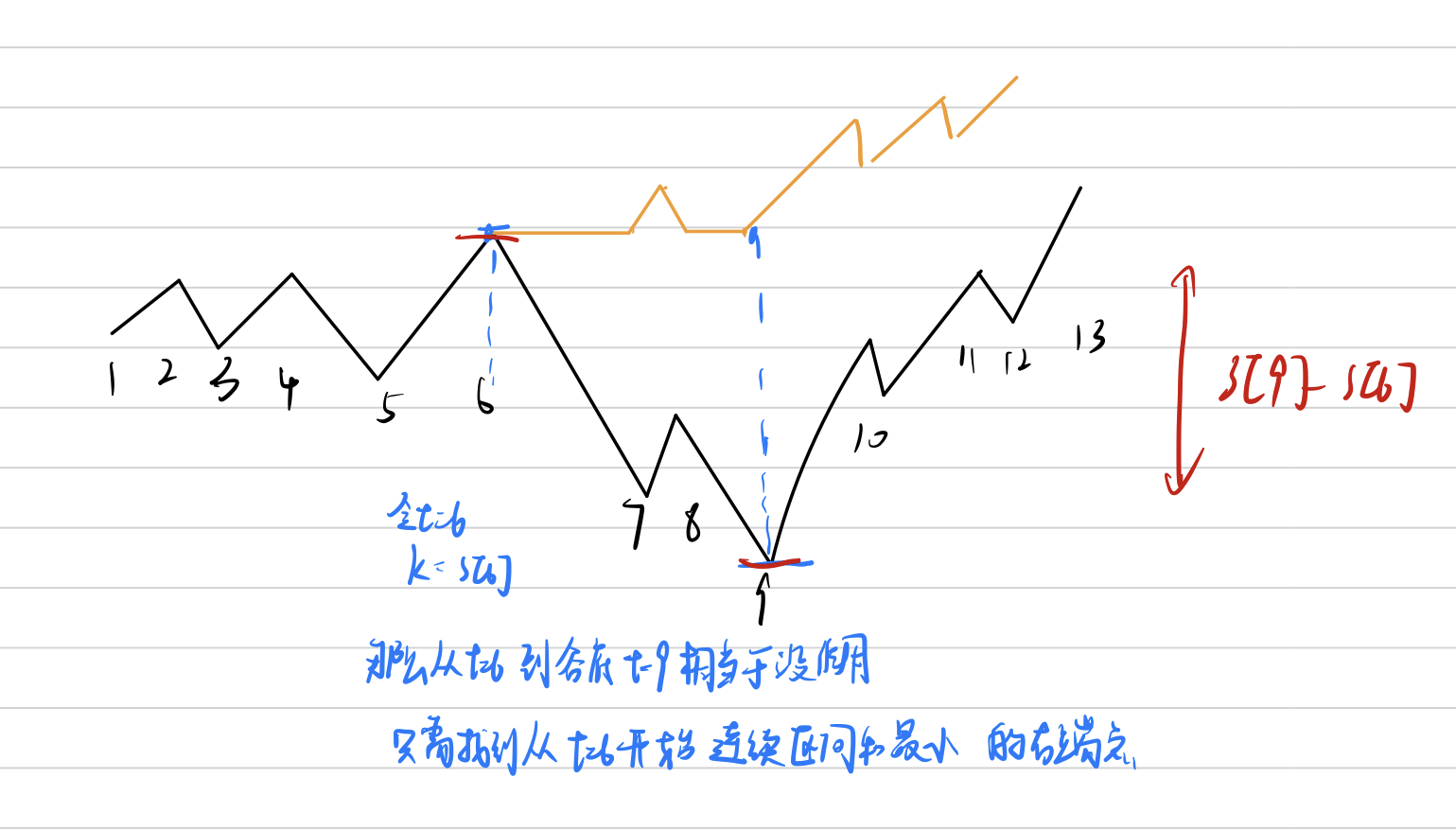
题意:给定一段分数变化序列ai ,i从1到n。你可以设定一个值k,score初始为0分。当score<k,时,score+=ai ,一旦score到达了k,从这之后,若 score+ai<k,则score=k,否则score+=ai 。求问在最终分数最高情况下k的取值为多少。
思路1:score需要累加达到k后,才能不低于k。所以k的取值范围为ai的n个前缀和。令k=s[i],这之后score不会小于k,对于从i后的每个位置t,score一定等于k+(后面所有的和-中间下降到k以下的部分)=k+某个后缀和。对于最后的结果,score一定是从k开始加直到加到末尾。问题转化为score=k+max(suf[t])
时间复杂度为O(n)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int n;
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
vector<ll>a(n+5);
vector<ll>s(n+5);
vector<ll>suf(n+5);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
s[i]=s[i-1]+a[i];
}
ll temp=0;
for(int i=n;i>=0;i--)
{
temp+=a[i];
suf[i]=max(suf[i+1],temp);
}
ll k=s[0];
ll score=suf[1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(score<=s[i]+suf[i+1])
{700
score=s[i]+suf[i+1];
k=s[i];
}
}
printf("%lld\n",k);
}
}
|
思路2:假设不附加k,那么score就为a1+a2+a3+...an 附加该规则后,我们从某一个时间t开始的一小段最大连续下落区间就不起作用 score=a1+a2+...al−1+ar+1+...+an,问题转化为求解最小子块和
E-Boxes and Balls
学完dp后再写
F-Swimming Pool
